Edge computing has become a buzzword in industry. With the rise of the Industrial Internet of Things, resorting to edge computing infrastructure now seems like a good option. We met with edge computing solutions provider Stratus Technologies to learn more.
“Edge computing is going to be the next industrial revolution” according to Arnaud Kurowski, Business Development Manager at Stratus Technologies. Arnaud drew on two sources to back up this affirmation . First, he mentioned the 2018 report by IDC Data Age 2025, The Digitization of the World: From Edge to Core that states that “By 2025, 175 zettabytes (175 trillion gigabytes) of data will be generated worldwide. Of this volume, 90 zettabytes will be generated by peripheral devices.”
He then alluded to Gartner’s 2018 report that says that “91% of current data is created and processed in centralized data centers. By 2022, approximately 75% of all data will need to be analyzed and processed in the periphery.”
So edge computing seems to be a keyword. But what does it mean exactly?
A definition of Edge Computing
Let’s try to understand. With the IIoT, we are generating and collecting data faster that we are able to analyze it because at the edge, resources are scarce and it becomes difficult for computing to handle all this data. Hence edge computing.
Edge computing is a form of IT architecture that involves processing data at the edge of the network directly where it is physically generated. Instead of transferring data generated by IoT-connected devices full of sensors (temperature, humidity…) to the cloud or a data center, data is collected and analyzed in real time on edge servers.
As computational resources are being stationed at the edge, they can filter or process data so that only what’s needed is transmitted between production control or enterprise systems and the cloud.
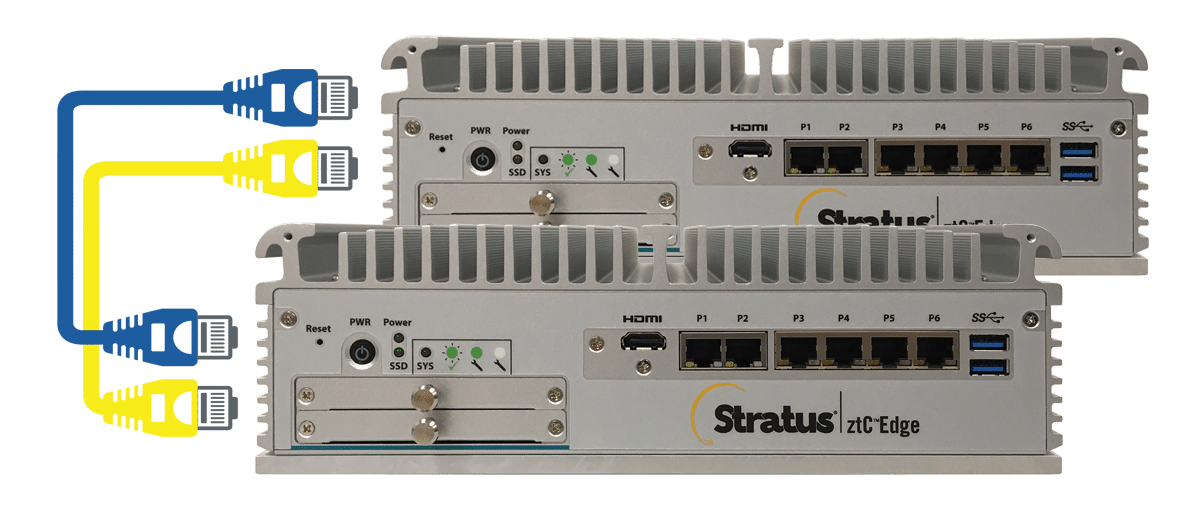
Stratus introduced their ztC Edge solution which is a zero-touch, virtualized computing platform that can be deployed on the factory floor. According to Arnaud Kurowski, this IT system has many advantages:
“First, it increases machine uptime preventing failures, it improves performance and profitability. It also allows to relieve bandwidth constraints or inherent latency. And it reinforces system security and reliability. The analysis of data at the edge reduces the latency and costs associated with sending data to the cloud which speeds up decision making.”
Thanks to this type of system, the manager of a factory can access data performance, speed, efficiency, consumption in real time, all of the information that could help him or her optimize operations.
In the oil and gas industry, this technology can for example help identify problems faster (for example a leak or an unusual temperature increase) which are very important considering the risks associated with this sector.
The value of edge computing also lies in its ability to avoid unplanned downtime and operational costs and ensure the performance of critical equipment, without compromising safety standards. Stratus’s system involves redundant servers to ensure data continuity, even if one of the servers fails.
Case Study: Edge Computing in a Turkish Power Station
Gürmat Elektrik is the largest geothermal power station in Turkey and needs to access to critical data in real time. They faced a situation where their previous IT infrastructure – with obsolete software, a slow SCADA system and security breaches – prevented them from accessing relevant information and data. They decided to implement Stratus’s servers along with Rockwell Automation’s software suite FactoryTalk.
For Mustafa Yalvaç, in charge of automation at Gürmat Elektrik, “Due to the network architecture, the old DCS system caused interruptions to the programmable automation controllers and computers. In addition, some diagnostics could not be monitored on the old SCADA system due to incompatibility.”
According to Mustafa Yalvaç, since the introduction of the new IT infrastructure, the data is now quickly accessible and more reliable, therefore increasing the performance of the station.
Edge Computing: the IT Rival of Cloud Computing?

So does this mean industry could get rid of cloud computing solutions? Despite what we might think, edge computing does not mean the end of cloud computing. It is more like either an alternative or an intermediary, explains Arnaud Kurowski.
“Edge computing allows to process data where it is collected. But after, this data can be sent to the cloud where it is enriched with artificial intelligence and machine learning, for example to predict failures, and then sent back to the edge server where the human operator can supervise it and use it for decision making.”
Edge computing does, however, reduce the need for IT support. Whereas computing in an industrial environment is complex and requires a team of IT professionals, edge computing is child’s play.
“With its built-in virtualization platform and availability layer, our solution is easy to deploy, manage and service. It can be installed in less than 30 minutes by an operator that is no IT staff. Even a kid could do it!”
The price of Stratus equipment is from €10,000 to €80,000.