Hannover Messe will only take place next April but we were able to get a glimpse of what to expect from the world’s industrial trade show. During a pre-press event last week organized by Deutsche Messe, we talked to various manufacturers about what they will showcase in April. The main innovations this year will focus on climate-neutral production, energy efficiency, and simplification of automation. Indonesia is also this year’s partner country and will feature 500 companies.
Hannover Messe will take place from April 17-21, 2023. DirectIndustry is collaborating with the fair this year. As part of this collaboration, we offer you, our readers, free tickets to the fair. Visit this page (text in French) to download your free ticket!
“Everybody is welcome to the Olympic Games of Innovation“. With these words, Dr. Jochen Köckler, Chairman of the Managing Board at Deutsche Messe AG, opened the Hannover Messe press preview conference last week in Hannover, Germany. This pre-event highlights the topics, trends, and innovations that are set to take center stage at the trade show in April.
This year, 4,000 exhibitors are expected to attend Hannover Messe, including 300 start-ups. The main theme of the 2023 edition will be the carbon-neutral industry. The main innovation trends this year will be related to smart and sustainable manufacturing, energy management, hydrogen, and how it is a game changer. 500 hydrogen industrial players are expected to attend the fair to showcase their products.
For Dr. Jochen Köckler,
“Only the interplay of these technologies will make it possible to sustainably safeguard our prosperity and at the same time drive climate protection forward.”
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will also be megatrends. Exhibitors will discuss the opportunities of new tools such as ChatGPT when applied to industry. According to Köckler,
“In the future, it is quite conceivable that AI will design a machine and the human will then check which adjustments are necessary for real operation. This saves time and offers considerable potential in view of the prevailing shortage of skilled workers.”
Indonesia is this year’s partner country. The country was scheduled for 2020 but the edition was canceled because of COVID-19. Indonesia became the partner country of the 2021 virtual edition of Hannover Messe. This year 2023, Indonesia will finally have the opportunity to be Hannover Messe partner country physically. For the occasion, Indonesian President Joko Widodo will travel to Germany along with 500 Indonesian companies.
What are the innovations that will make the news in April? Here is what we found during the press event.
1/ Climate-Neutral Production
This is the mega theme. Climate-neutral production is a crucial step in combating climate change and reducing the carbon footprint of industrial activities. Achieving CO2-neutral production typically involves a combination of measures, such as using renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and implementing carbon capture and storage technologies. The objective is that the manufacturing process does not result in net greenhouse gas emissions.
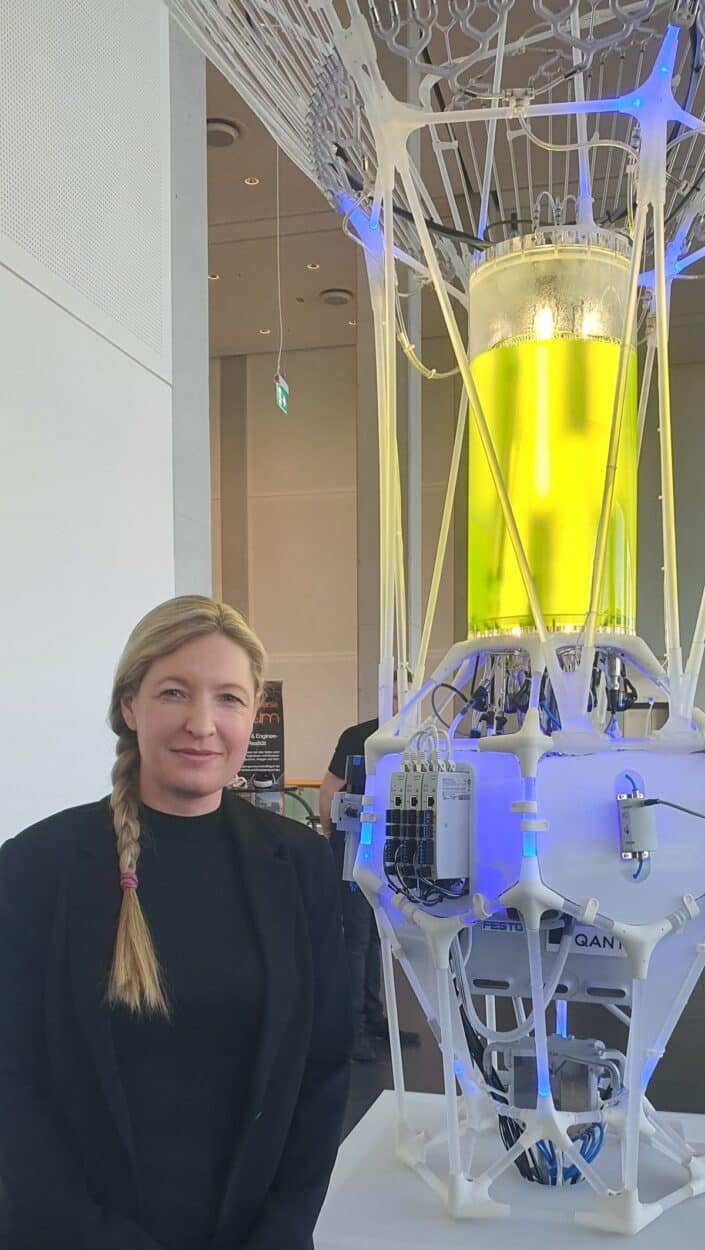

This is what Festo will be showcasing in Hannover Messe this year, for the second year in a row. The company has developed a photobioreactor to automate the cultivation of biomass.
We spoke with Dr. Nina Gaissert, an expert in industrial biologization at Festo.
“This is our PhotoBionicCell and this is where we grow algae. Algae has been used for millions of years as food. But they have a much bigger potential. They have a role to play in creating a real climate-neutral circular economy. We try to learn from nature to improve technology.”
Algae have emerged as an unlikely hero in the fight against climate change. In their natural state, they are already highly proficient at photosynthesis and can absorb up to ten times more carbon dioxide than land plants. By utilizing bioreactors equipped with advanced sensors, control technology, and automation, the efficiency of algae can be amplified up to a hundred times more than land plants.
The liquid containing the algae is pumped upwards and distributed evenly across surface collectors before being cycled back to the cultivator. As the algae cells circulate, their chloroplasts use photosynthesis to transform sunlight, CO2, and water into organic, recyclable materials and oxygen. This closed-cycle method of biomass cultivation is extremely resource-efficient and highly effective.
“We can generate oils, food, supplements, and even bioplastics. A part of the bioreactor is made of bioplastics that come out of the bioreactor. So we can substitute fossil resources by growing algae today”.
The bioreactor is equipped with many sensors to measure the temperature inside the reactor, the CO2 concentration, the O2 concentration, the Ph, the light intensity… The data is then sent to the controller to make models to predict the behavior of the cells.
Festo: Halle 7, Stand D31
2/ Preventing Occupational Health Risks
Workers in industry are exposed to various occupational health risks. Some of the most common risks include physical hazards, such as noise, vibration, and exposure to extreme temperatures, as well as chemical hazards, such as exposure to toxic chemicals and fumes. In addition, poor ergonomic design of workstations and repetitive movements can cause musculoskeletal disorders.
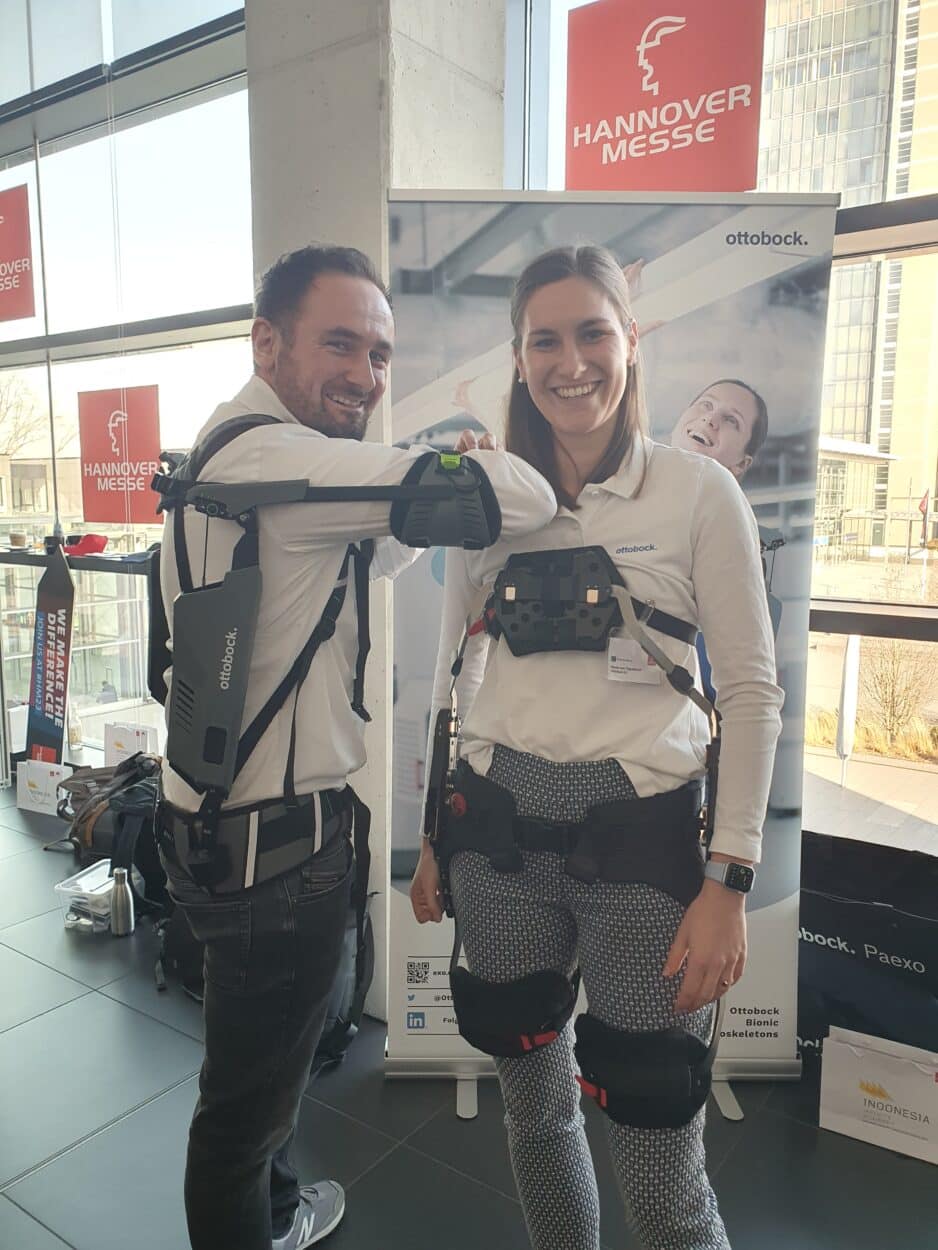

To mitigate these risks, it is crucial that employers prioritize occupational health and safety in their workplaces. Many employers are now taking steps to ensure the safety and well-being of their employees, and for example, equip them with exoskeletons.
Ottobock SE manufactures exoskeletons for industrial workers.
We talked to Nicola von Tippelskirch, an ergonomics specialist at the company. She presented us with two exoskeletons of their portfolio, the Ottobock Shoulders and the Ottobock BackX.
“With the BackX we take the weight force from the lower back. When lifting heavy loads we can prevent for example disk injuries.
This exoskeleton which weighs 3.3 kg is mostly used by workers in the logistics industry, for packing, loading, and unloading containers.
“The Ottobock Shoulder is used in the case of overhead work. In the French market, it is used for example by the French train company SNCF, or by aviation companies. It helps workers carry heavy loads and helps them realize overhead tasks.
This exoskeleton is only 2 kg. None of the exoskeletons by Ottobock are automated.
“We don’t have automated systems, it is purely a mechanical system. We take away parts of the force but not all. We want the human body to still work, the muscles are supposed to move, we just remove the things that are bad for the human body.”
The exoskeletons cost between 4000 and 6000 euros each.
Ottobock: Halle 7, Stand A28/1
3/ Simplifying Automation
The use of robots has become increasingly common in industries. Robots are designed to perform repetitive and monotonous tasks without getting tired, bored, or distracted. This makes them ideal for tasks that require high precision and accuracy, such as assembling small parts, painting, or quality control. By automating these tasks with robots, companies can reduce human error and increase productivity, which can result in significant cost savings.
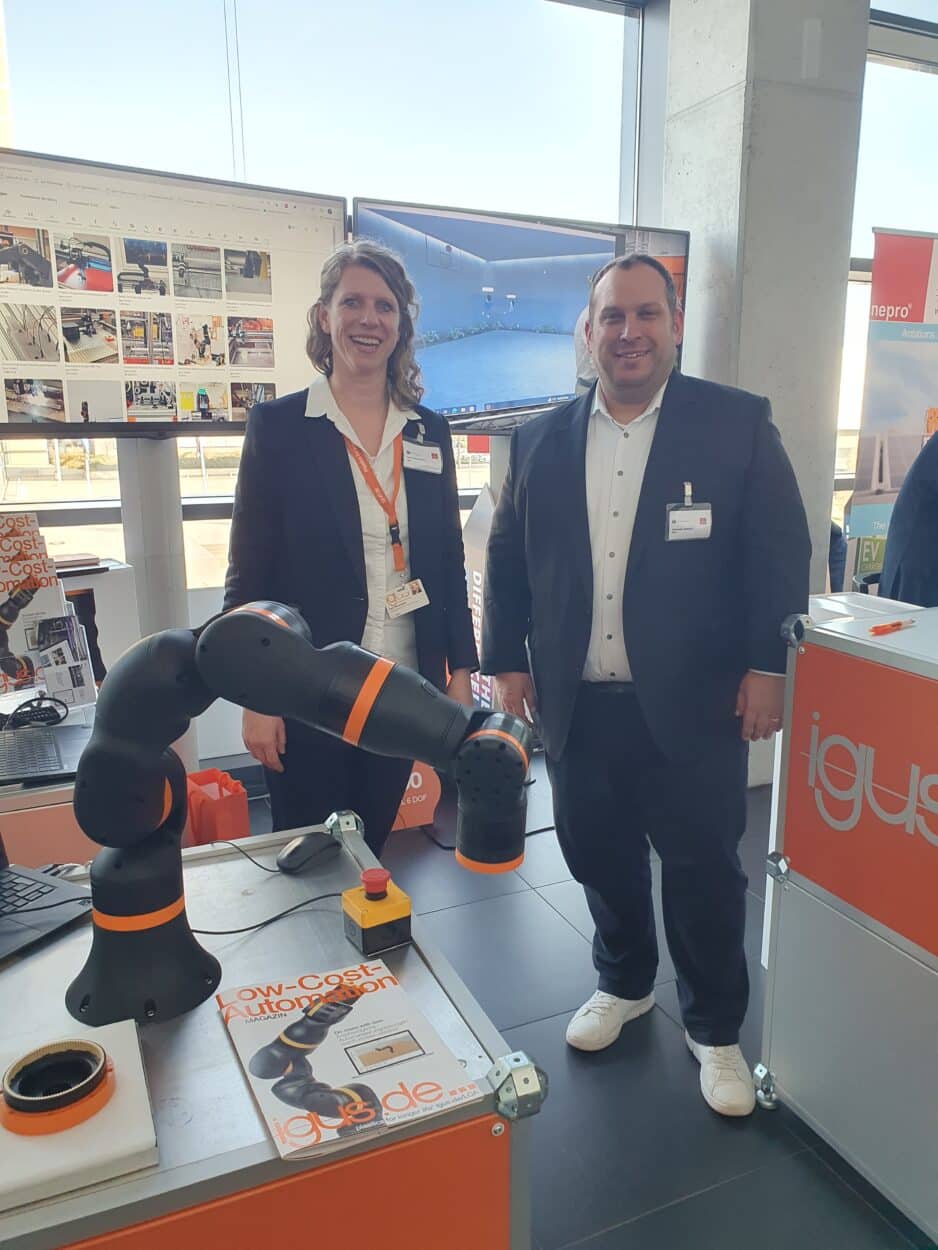

However, a robot needs to be programmed which can be difficult for a company, especially when they don’t have specialized skills. Some companies are aimed at making automation easy to implement and cheap for everyone.
This is what igus, the specialist in motion plastic cables, is offering to the market. They have developed ReBeL, a low-cost cobot, less than 5000€, that does not need the user to have any programming skills.
According to Alexa Heinzelmann, Head of International Marketing at igus,
“This cobot is made of motion plastics and this is why we are now in the cobotics industry. We are using our motion plastic expertise to build 6-axis robotics arms like this one. We are making this cobot for small companies who are not into programming. We want to help them automate some of their productions easily and in a cheap way.”
This cobot is not expensive, less than 5000€, and if it is that cheap it is because it does not involve any metal components inside, except the motor. Everything else is made of affordable plastic parts.
For Alexander Mühlens, Head of the business unit low-cost automation
“This cobot is low cost but if you need a lot of programming after, then it’s not affordable in the end. So we do the programming for you. It is included in the 4900€. If you did not know anything about robots or coding so far, you can ask us and we will build an automation solution for you.”
The cobot weighs 8.2 kg and has a payload capacity of 2 kg. It can be put on a stationary table as well as on a mobile platform.
“If you need to pick and place within 6 seconds, this is the right solution. If you need faster times, you need to choose another robot. We concentrate on low-cost, affordable products made in Europe. And we concentrate on easy applications. We don’t focus on very precise millimeter applications. And we don’t make our cobots pick and place cars and heavy loads. But if you are looking for all the other applications, this could be the right choice.”
At the moment, igus low-cost cobots are used by machinery industries for inspections, metrology, and easy pick-and-place applications around conveyors. Vertical farming is also showing interest. igus has also installed some units inside small bakeries to automate some processes.
igus; Hall 6, Stand E26
4/ Indonesia: Hannover Messe 2023 Partner country
Indonesia, with its 16,000 islands, is one of the world’s countries most directly affected by global warming. The impact of climate change is already affecting the development of the country’s industry. Jakarta, too exposed to rising waters, can no longer remain the capital of the country. The new capital will move to the island of Borneo. Yet the country has the ambition to become the world’s 10th-largest economy by 2030.
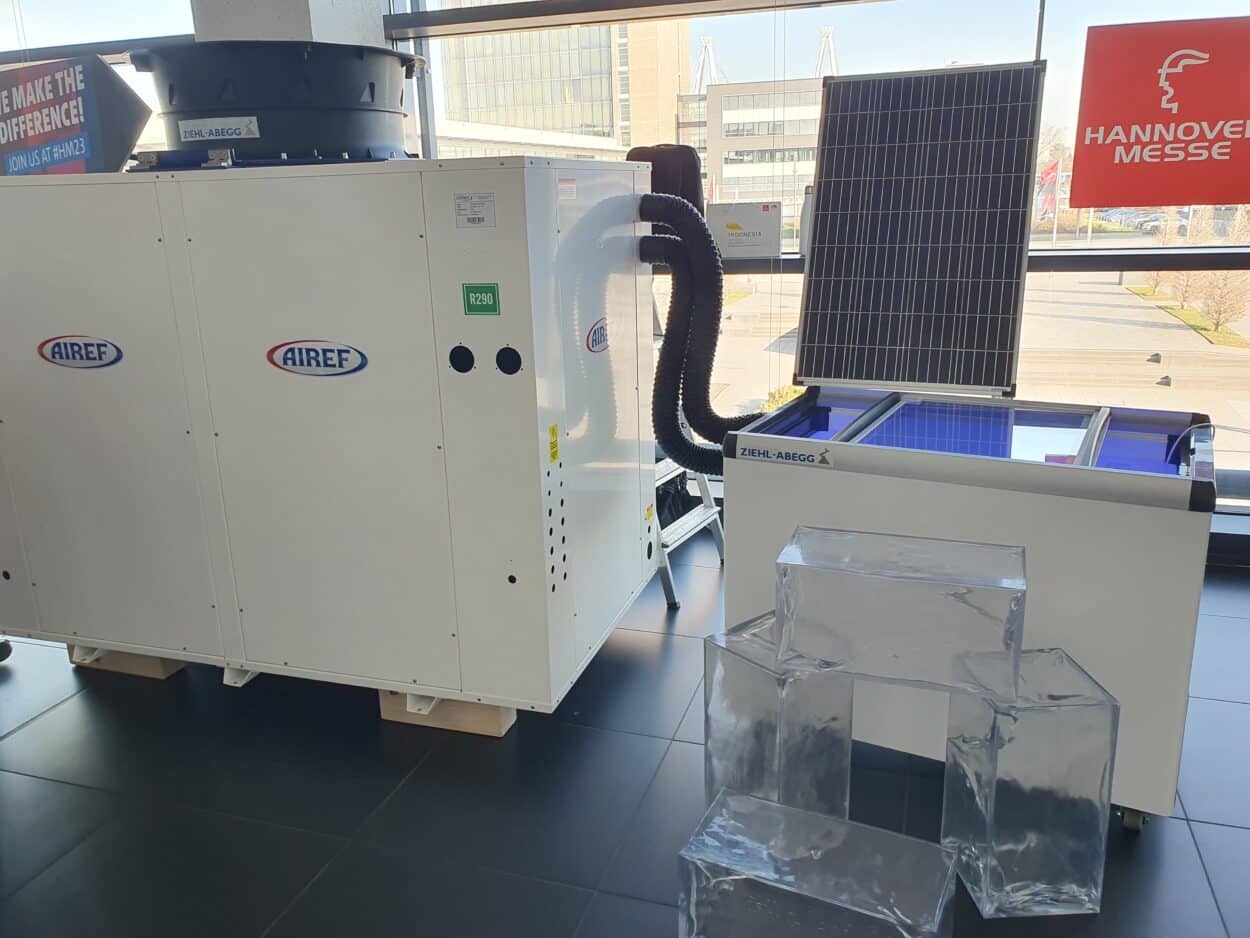

At this year’s Hannover Messe, 500 Indonesian companies will be presenting their innovations. One of the initiatives that caught our eye is done in collaboration with a German company. It is a solar ice maker aimed at Indonesia’s small-scale fishermen.
Indonesia is the world’s second-largest fish producer. However, small-scale fishermen who employ sustainable fishing methods struggle to transport their catch to consumers due to inadequate refrigeration facilities. To conserve fish stocks and secure the livelihoods of fishermen in remote areas, the key is to maintain a continuous cold chain for the catch.
German company Ziehl-Abegg, in collaboration with several Indonesian, German, and other European companies developed a solar-powered ice-making machine aimed at implementing seamless refrigeration chains for fishermen.
For Kai Rittman, Sales International project engineering at Ziehl-Abegg,
“We developed a technology that produces electricity with solar panels. We designed a highly efficient fan that is using low solar power to produce enough cooling energy which is used to freeze down the water. This involves propane gas which goes into the system to cool the water and freeze the cubes. It takes 10 hours to make the cubes.”
The project began in 2016 and the pilot plant launched successfully in 2018. The first commercial unit is already operating in Indonesia.
The price of the machine is around $250 000.