By Philippe Gérard – Product & Segment Manager – Motion at Bosch Rexroth France
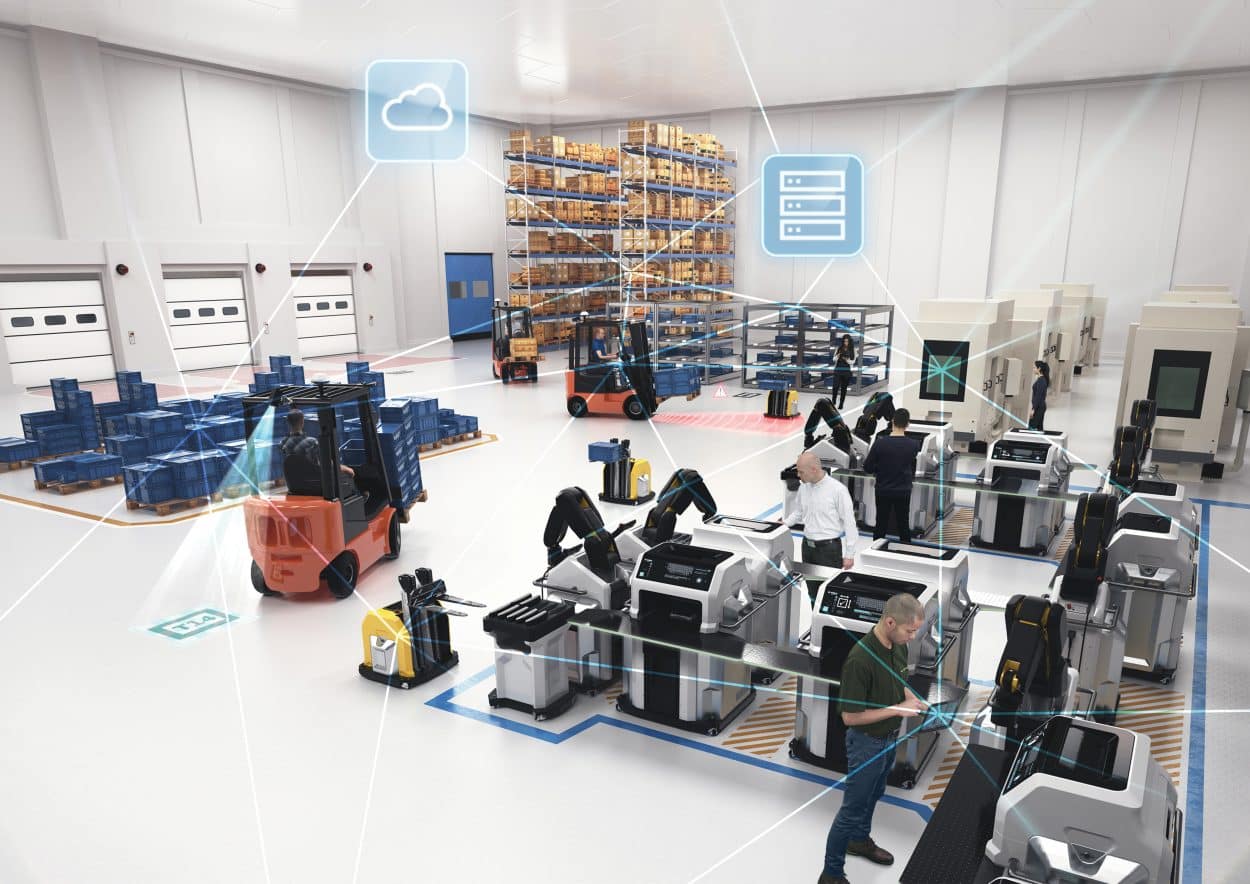
Talking about the industry of the future, or Industry 4.0, without mentioning automation is difficult. Automation is maturing, around major trends that will instigate major changes in the medium term – which we need to keep abreast of to keep the pace – in an industry that is rapidly developing its innovation.
01. Opc UA Protocol and 5G

In industrial automation, OPC (Open Platform Communication) and OPC UA (Unified Architecture) protocols for connected objects represent the achievement of exemplary joint work, started in 1996, between a majority of Industry 4.0 stakeholders to secure and structure data flows in industrial automation.
Indispensable for the transmission of data to decision-making computer systems, the dissemination of instructions in top-down mode, and machine-to-machine communication, these protocols are now evolving towards a dynamic of real-time transmission under the influence of the development of connected sensors and embedded software. Data will no longer be transmitted in packets but in more continuous flows. This is the advent of a new protocol called OPC UA TSN.
This new protocol will require an efficient communication network. This could conventionally be wired, or wireless with the advent of 5G. Real-time communication will be the fundamental technology for the development of edge computing, and it certainly represents one of the major advances in Industry 4.0 thanks to enhanced data transmission security, reduced storage costs, and greater responsiveness.
02. Hyper-Adaptability of Production Lines and On-The-Fly Recalibration
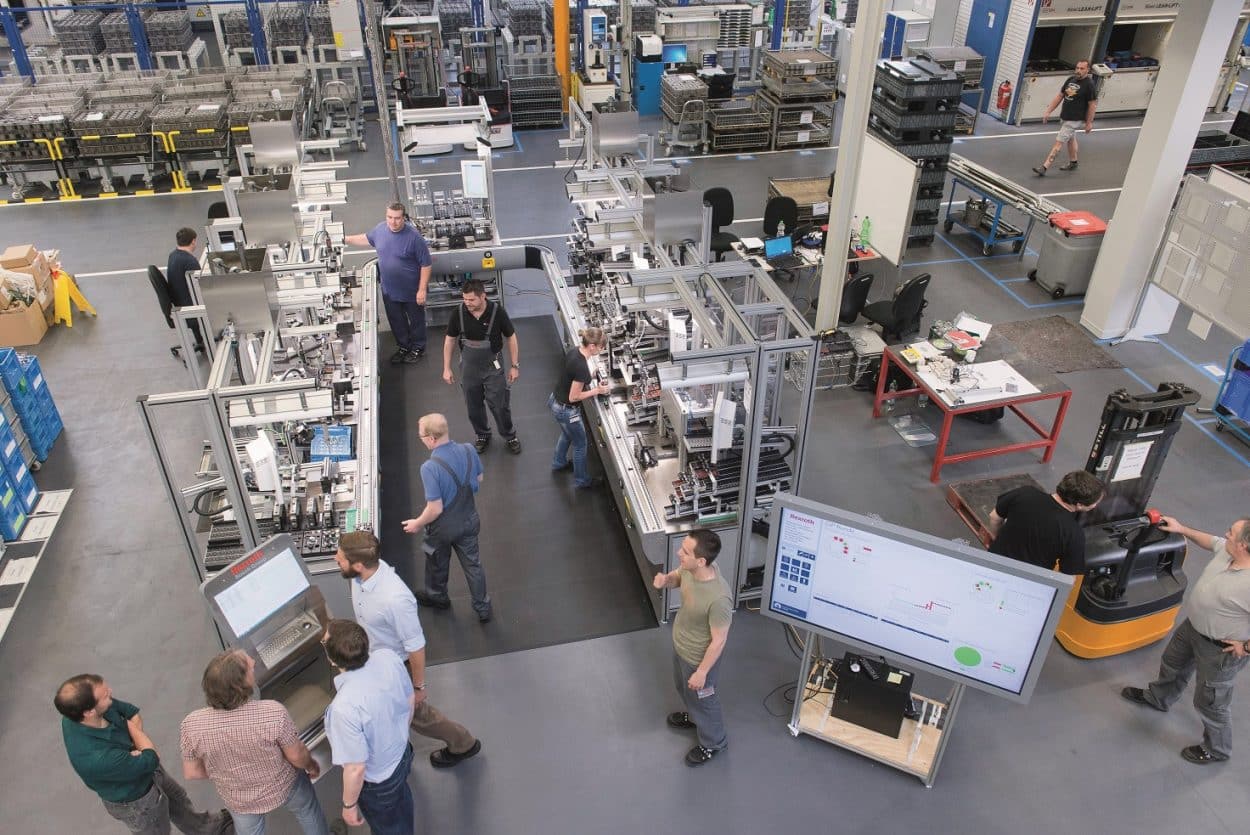

Equipment flexibility is another major trend in Industry 4.0. We are witnessing a change in needs favoring the production of mini-series and more product customization. The ability of a company to modify its production, according to ever more diversified models, is a challenge that some have already taken up, succeeding in coordinating very short production times of a just few minutes by chaining them. Record time recalibration of equipment concerns as much automation and digital controls as actuators and transfer systems.
This is why the connectivity response is essential to ensure the ideal transmission of commands from the ERP to all chain components, and this is where the OPC UA protocol demonstrates its value.
The full integration of a machine into the information system of an industrial environment allows a production strategy to be automatically modified while synchronizing the line’s various components through very efficient inter-machine communication.
Technological developments now also make it possible to enrich new features with automation that has hitherto been little or not scalable: just as machines adapt, automation also adapts, with the addition or removal of features by systematically updated software applications.
03. Data Available for Machine Ecosystems (Smart Conveying, AGVs, Cobots)
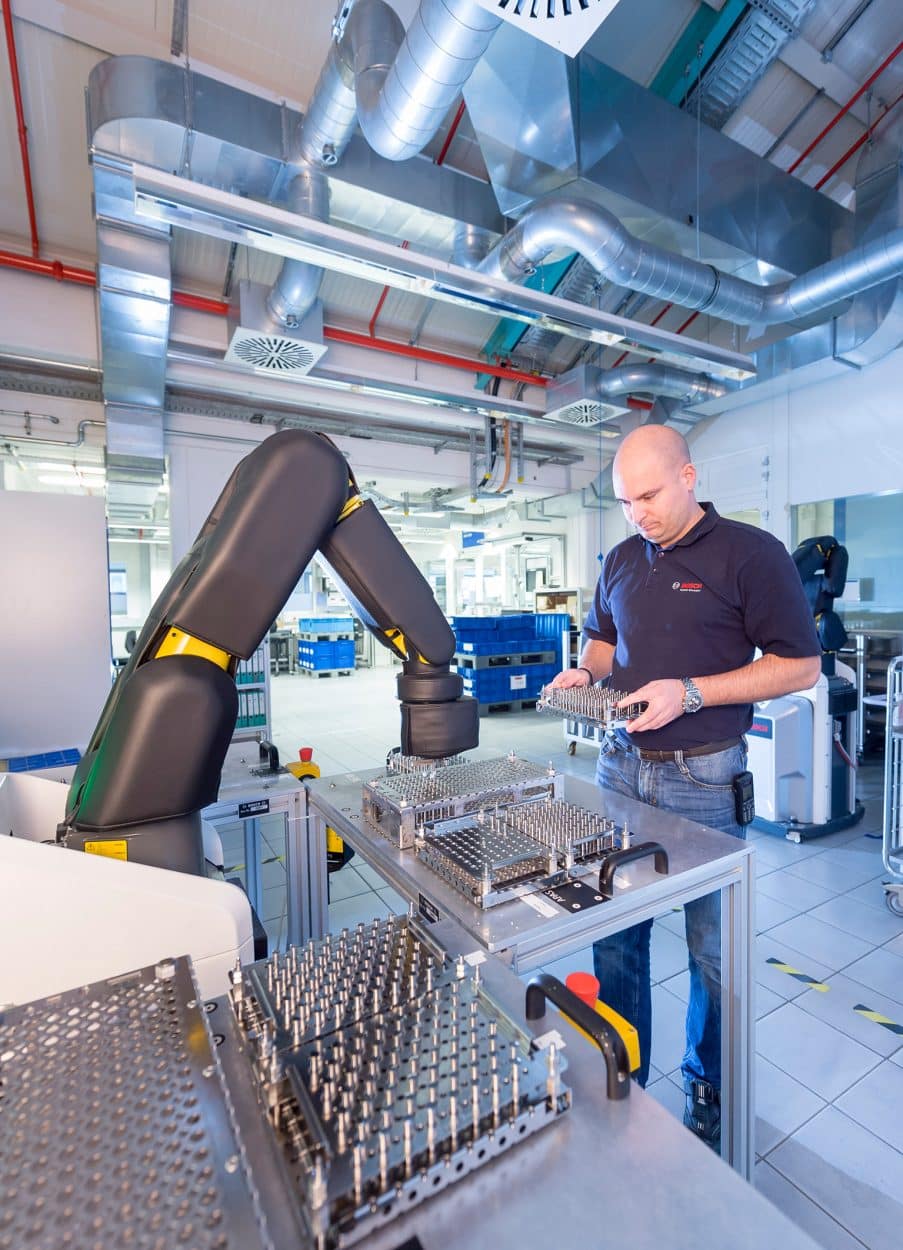

Data production, ever increasing due to equipment performance and its integrated connectivity, is only relevant if the data is shared with the machine’s ecosystem: smart conveying, AGVs, cobots, etc.
The gradual introduction of smart conveyors, the magnetic properties of which make it possible to adapt the conditions for picking up, depositing, assembling or screwing, and transporting from one production line to another, is added to the participation of AGVs at the start and end of a production line. This combination makes it possible to maintain the pace of diversified production, while responding to the physical constraints of a building.
The constant adaptation of machines and their ecosystem is one of the major and inevitable directions for the automation of the future. It makes it possible to define and optimize the trajectories of AGVs in a constrained space: the machine adjusts itself automatically thanks to a smart conveyor and adapts the operation of cobots as working partners of operators.
This adaptability is fuelled by the massive flow of data available for better traceability of events and a greater understanding of machine behavior.
04. New Programming Languages and New Recruitment Profiles
With the massive deployment of connectivity to ensure the integration of machines for fluid, easy, and rapid communication, how programming and automation is designed is also changing, as are the profiles recruited by companies.
We need to support the shift from conventional automation trades to more diversified profiles who can better respond to future challenges combining robotics, mechanics, and electronics through the lens of software and inter-connectivity. As such, new computer-oriented languages, such as Python and Java, are emerging in current automation solutions. Machine programs will henceforth be constructed by independent functional applications, coded with the most suitable language.
This change in profiles should be viewed as an asset. It allows us to take a fresh look at the design of automation systems and to take a less academic approach than we did five or ten years ago. Agile application development is a cornerstone that will undoubtedly benefit the entire industrial sector.
There will be so many other topics to discuss from the perspective of industrial automation. For example, the development of functional safety is important from a zero complete stop perspective. 3D printing is of great interest in the manufacture of mechanical parts given the materials available today. What emerges is a permanent emulation and the assurance that Industry 4.0 has not finished surprising the world.