Power sources are important. From providing energy to electronic devices to ensuring uninterrupted operations, different types of power sources are required for various purposes. There are different types of technologies available: power supplies, UPS, and batteries. Since it is not always easy to choose the right equipment in front of a multitude of manufacturers, we have produced several buying guides with tips and recommendations to help you make the right purchasing decision.
Hicham Dhouibi, Soukaina Okacha, Francesco d’Amore, Vincent Vilarrasa, Monica Hutchings, and Cédric Vialle contributed to these buying guides.
DirectIndustry offers a free online buying guide service to advise you on what you need to know before you buy a product or request a quote. The goal is to give business leaders, industrial buyers, and decision-makers detailed descriptions, key criteria, standards, and prices of industrial products to facilitate your comparison of quotes and your choice of suppliers in order to make the right purchasing decision. Our buying guides are written by our professional journalists and in-house industry analysts in an independent and impartial way. None of the content is sponsored or promotional.
We focus on three common types of power sources: batteries, power supplies, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
Batteries are widely used in electronic devices, from small portable devices to large machines. They are designed to store electrical energy and provide it to devices when needed.
Power supplies convert the alternating current (AC) voltage from the power grid into a stable direct current (DC) voltage suitable for electronic devices.
UPS, short for uninterruptible power supply, provides backup power during power outages. Unlike batteries and power supplies, UPS systems offer almost instantaneous protection against power interruptions by utilizing energy stored in batteries.

How to Choose The Right Power Supply?

A power supply supplies electrical energy to electronic devices, guaranteeing that the supplied power matches their requirements, irrespective of the characteristics of the electrical grid. It takes in AC voltage from the wall outlet or a DC voltage from a battery and converts it into a stable, low-voltage DC output that can be used by the device.
They are necessary to power devices including computers, servers, routers, telecommunication equipment, and manufacturing machinery, and are used in a wide range of industries, from electronics and telecommunications to automotive and aerospace.
- WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF POWER SUPPLIES?
- WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT POWER SUPPLY TECHNOLOGIES?
- WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT COMPONENTS OF A POWER SUPPLY?
- WHAT DO YOU HAVE TO AVOID?
- WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT WAYS A POWER SUPPLY CAN BE ASSEMBLED?

How to Choose The Right Battery?
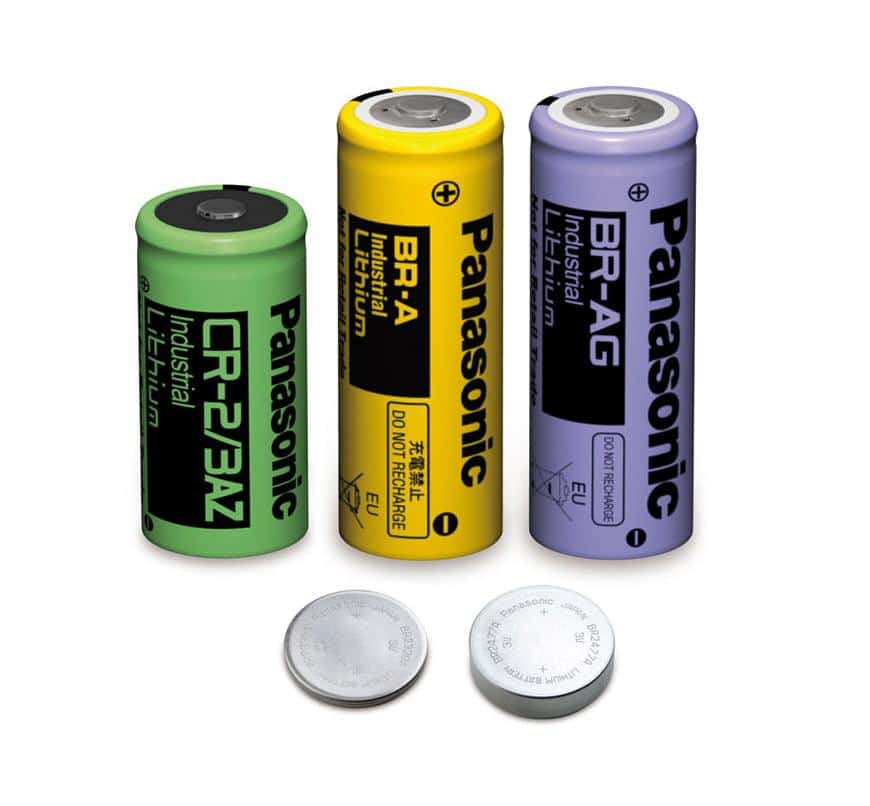

A battery is a device that comprises one or more electrochemical cells with external connections to power electrical devices.
Rechargeable batteries are available in various sizes, from button cells to megawatt systems that stabilize electrical distribution networks. They utilize different combinations of electrode and electrolyte materials, such as lead-acid, nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), lithium-ion (Li-ion), and lithium-ion polymer (Li-ion polymer).
This guide covers both rechargeable and non-rechargeable (alkaline) battery technology
- HOW TO CHOOSE A BATTERY?
- HOW DO YOU CORRECTLY CALCULATE THE SIZE OF A BATTERY?
- WHY CHOOSE A LITHIUM BATTERY?
- WHY CHOOSE A LEAD BATTERY?
- WHY CHOOSE A NICKEL BATTERY?
- WHY CHOOSE AN ALKALINE BATTERY?

How to Choose The Right UPS?

A UPS, an uninterruptible power supply, is an electrical device that offers backup power in case of a power source failure. Unlike auxiliary or backup power systems, a UPS provides almost instantaneous protection against power interruptions by utilizing energy stored in batteries, supercapacitors, or flywheels.
They are commonly used in critical systems such as data centers, medical facilities, and industrial processes, where even a momentary power failure can have catastrophic consequences.
Although the run time of most UPS is relatively short, usually only a few minutes, it is adequate to start an emergency or auxiliary power source or to safely shut down the protected equipment. Typically, a UPS is employed to safeguard computing equipment such as computers, data centers, telecommunications equipment, and other electrical equipment in situations where a power failure could lead to significant service disruptions or data loss.
![[BUYING GUIDES] Battery, Power Supply, UPS: How to Make the Right Choice?](/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/iStock-1446911643-1250x769.jpg)